Category: Theology
-
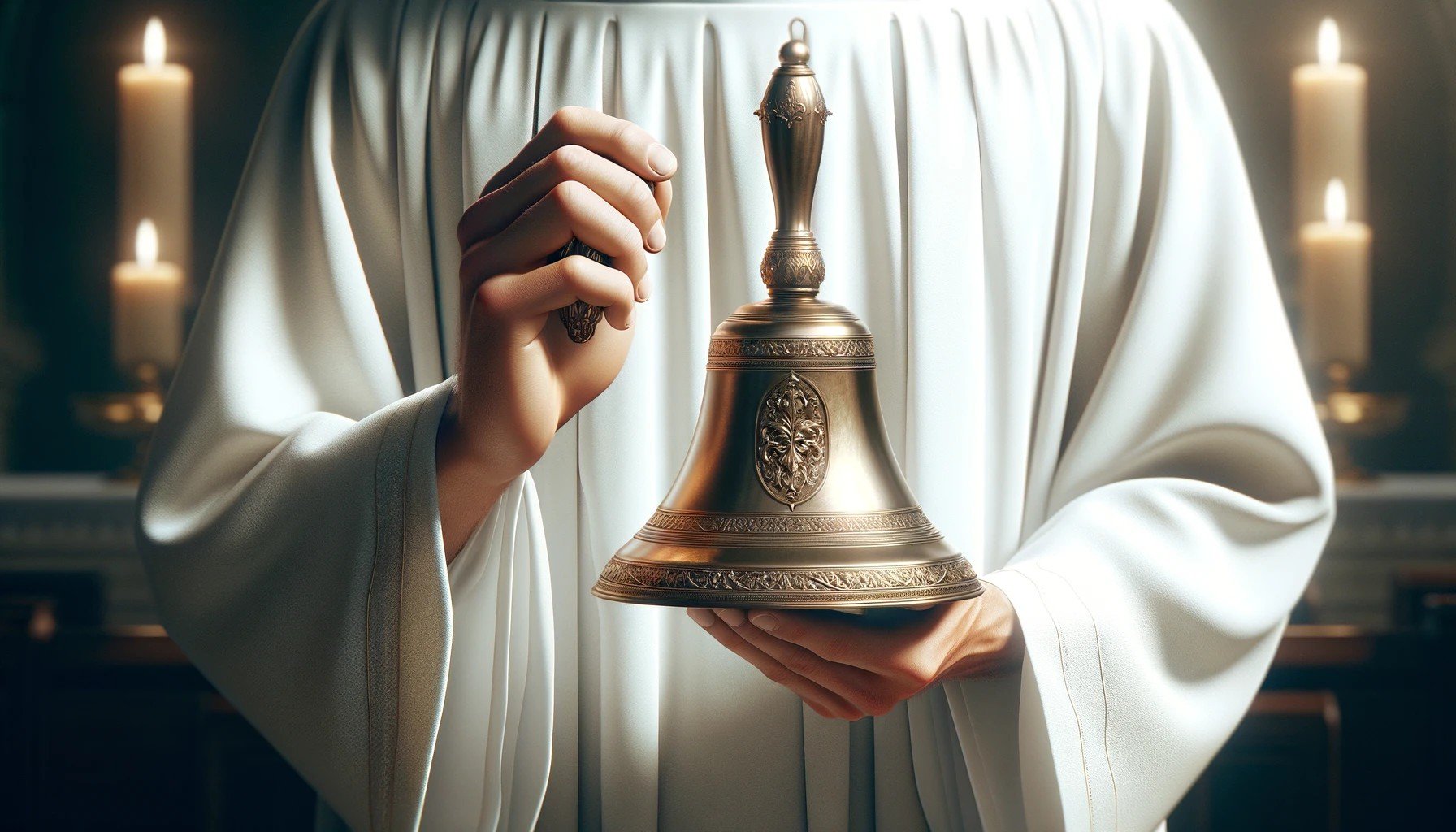

Know Theology |Why Do Catholic Churches Ring Bells During Communion?
Read More: Know Theology |Why Do Catholic Churches Ring Bells During Communion?Catholic Theology Series The ringing of bells during Catholic Mass holds a profound significance that transcends mere auditory stimulation. It is a practice deeply rooted in tradition, symbolism, and practicality. The melodic chimes of the bells resonate through the sacred space, serving as a poignant reminder of the spiritual journey undertaken during the Communion service.…
Search
Popular Posts
-
The Bible is a Catholic Book!
Download below for Free Powered By EmbedPress
-
Which Bible Should We Read?
Please Download Below! Powered By EmbedPress
Categories
Archives
Tags
#Miracles (106) 2023 (4) 2024 (4) approved miracles (2) catholic (148) catholic blog (395) catholic meditations (7) catholic miracles (391) catholic motivation (2) catholic news (385) catholic prayers (4) CatholicSeers (373) catholic vlog (394) catholic websites (6) Eucharistic miracle (2) fr jim blount (3) GisellaCardia (11) hamas (3) imitation of christ (2) Israel (4) israel live (5) Israel news (9) jesus (3) jesus christ (4) Latest messages (11) lent 2023 (10) lent 2024 (4) lent homily (2) lent retreat (4) lent retreat 2023 (3) Lourdes (2) messages from god (6) MessagesFromHeaven (381) miracles of catholic church (2) mother and refuge (2) ourlady (329) OurLadyApparitions (22) our lady of lourdes (2) Pope (2) POPE francis (3) pope francis news (2) prayers (3) real miracles (367) sacred heart of jesus (2) The Miracles of Lourdes (2)